Understanding Digital Transformation in Banking
Digital transformation in banking is the process through which financial institutions integrate modern technologies to enhance their services, improve operational efficiency, and meet evolving customer expectations. It goes beyond simply digitizing existing processes; it’s about rethinking how banking works, leveraging innovations like cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), big data, blockchain, and automation to reshape the entire banking experience.
At its core, digital transformation in banking is driven by the need to deliver more personalized, efficient, and accessible services to customers. This transformation allows banks to improve customer engagement through online platforms and mobile apps, streamline back-office operations through automation, and enhance security through advanced encryption and AI-powered fraud detection systems.
The goal of digital transformation is not only to meet the demand for speed, convenience, and personalization but also to ensure that financial institutions remain competitive in a rapidly changing market. By embracing digital technologies, banks are able to foster innovation, stay agile, and provide more dynamic solutions to customers.
Key Technologies Revolutionizing Banking
The digital transformation of banking is driven by several cutting-edge technologies that are reshaping how banks operate and deliver services. These technologies not only improve efficiency but also enable banks to provide innovative and personalized customer experiences. Here’s a look at the key technologies that are revolutionizing the banking sector:
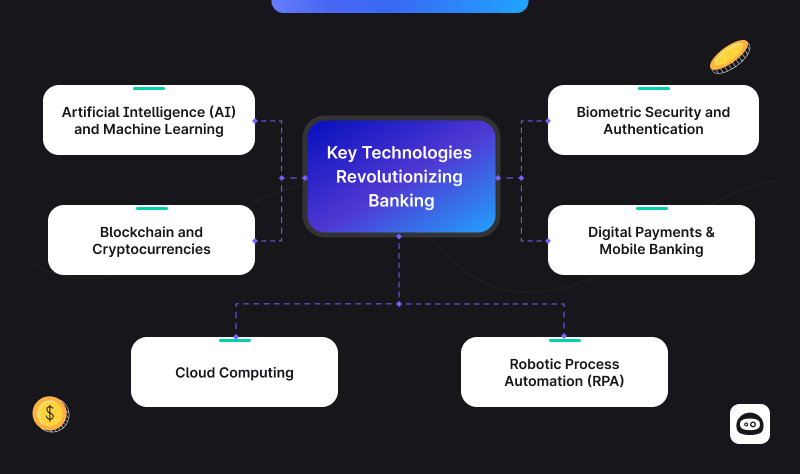
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are at the forefront of banking innovation. AI refers to systems designed to simulate human intelligence, while ML enables machines to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. In banking, AI and ML are used for:
- Customer service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer inquiries 24/7, providing immediate assistance and reducing wait times. They also provide personalized responses based on the customer’s history.
- Personalized banking experiences: AI can analyze a customer’s financial behavior and recommend personalized products, such as tailored loan offers, investment advice, and savings plans.
- Fraud detection: Machine learning algorithms detect unusual transaction patterns in real time, helping banks spot and prevent fraudulent activity before it escalates.
- Credit scoring: AI and ML are used to assess an individual’s creditworthiness by analyzing a broader set of data points, including transaction history, rather than just relying on traditional credit scores.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and immutable way. While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are the most famous use case of blockchain, it’s also revolutionizing the banking sector by offering several key benefits:
- Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes it highly secure and resistant to fraud and hacking. Banks use it to create tamper-proof transaction records.
- Cross-border payments: Blockchain facilitates faster, cheaper, and more secure international money transfers. Unlike traditional methods that can take several days and come with high fees, blockchain transactions can be processed almost instantly, reducing costs and delays.
- Smart contracts: These self-executing contracts automatically trigger actions when certain conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and enhancing operational efficiency.
- Cryptocurrency adoption: Many banks are now exploring how to integrate cryptocurrencies and blockchain into their offerings, creating new products and services for customers interested in digital assets.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as storage, processing power, and software over the internet, rather than on physical servers. For banks, cloud computing provides:
- Scalability: Banks can scale up or down based on demand without needing to invest in costly infrastructure or hardware.
- Cost-efficiency: Cloud solutions reduce the need for expensive on-site IT infrastructure and maintenance. Banks pay only for the resources they use, making it more affordable and efficient.
- Agility and innovation: With cloud computing, banks can quickly launch new services and products, responding faster to customer demands and market changes.
- Data storage and security: The cloud offers secure and flexible storage solutions for vast amounts of customer and transactional data. With encryption and advanced security measures, it ensures data is protected while being easily accessible.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to the use of software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks traditionally performed by humans. In banking, RPA is used for:
- Back-office operations: Tasks like data entry, account reconciliation, and loan processing can be automated using RPA, allowing banks to reduce human error and improve efficiency.
- Compliance: RPA helps banks manage regulatory compliance more efficiently by automating the process of monitoring transactions, filling out forms, and generating reports.
- Customer service: RPA can be used to process requests, such as updating account details or issuing account statements, reducing processing times and improving the customer experience.
- Cost reduction: By automating manual tasks, banks can lower operational costs, redirecting resources to more value-adding activities.
Digital Payments & Mobile Banking
Digital payments and mobile banking have completely transformed how customers interact with their financial institutions. These technologies offer:
- Convenience: Mobile banking apps and digital wallets enable customers to make payments, transfer funds, and manage their accounts from anywhere, at any time.
- Contactless payments: Using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, customers can make instant, secure payments by simply tapping their mobile devices or cards at payment terminals.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments: Mobile apps like Venmo and PayPal have made it easy for individuals to send money directly to one another without needing to visit a bank branch.
- Real-time transactions: Digital payment systems offer faster, more efficient processing of transactions, including the ability to instantly transfer funds between accounts or pay bills online.
- Security: Mobile banking apps are equipped with advanced security features such as two-factor authentication (2FA), encryption, and biometric authentication, ensuring that customer information remains protected.
Biometric Security and Authentication
Biometric security refers to the use of unique physical or behavioral characteristics to authenticate a person’s identity. Banks are increasingly using biometric methods to enhance security and simplify the authentication process:
- Fingerprint scanning: Many mobile banking apps and ATMs use fingerprint recognition to securely grant access to customer accounts.
- Facial recognition: Some banks use facial recognition technology as a secure and convenient method for customers to log into mobile banking apps or access ATMs.
- Voice recognition: Certain banks offer voice biometrics as a way for customers to authenticate themselves over the phone without needing to remember passwords or PINs.
- Enhanced security: Biometric authentication is more difficult to replicate or steal compared to traditional passwords, offering a higher level of security for sensitive banking transactions.
These technologies are drastically improving efficiency, security, and the overall customer experience in the banking industry. By embracing innovations like AI, blockchain, and mobile payments, banks are not just staying competitive but paving the way for a more accessible and modern financial ecosystem.
Strategies for Driving Digital Transformation in the Banking Industry
Digital transformation is not just about implementing new technologies, it’s about fundamentally changing how banks operate and engage with customers. To successfully drive digital transformation, banks need a comprehensive strategy that incorporates technology, organizational change, and customer-centric approaches. Here are key strategies for successfully implementing digital transformation in the banking industry:
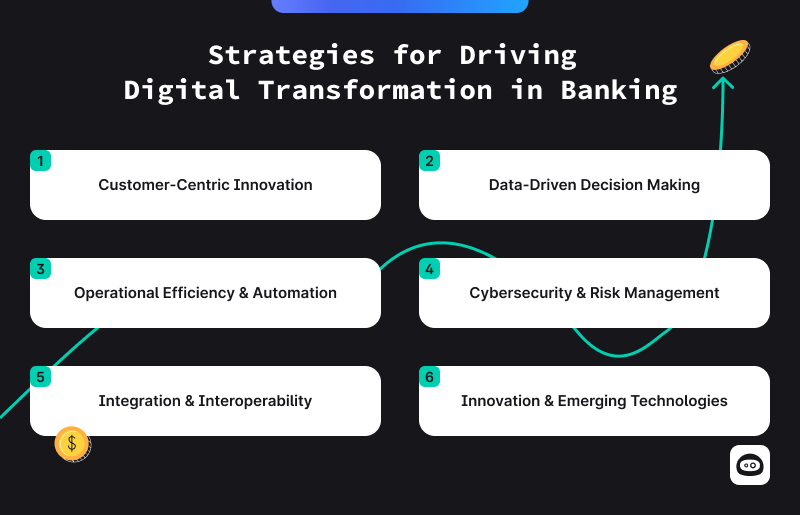
- Customer-Centric Innovation
At the heart of digital transformation in banking is a focus on customer-centric innovation. As consumers become more digitally savvy, their expectations of banking services continue to evolve. Banks must prioritize the development of personalized and convenient services to stay competitive.
Key Strategies:
- Personalized Products & Services: Leverage customer data and AI to offer tailored products and services, such as personalized savings plans, investment recommendations, or loan offers based on an individual’s financial behaviors.
- Omnichannel Experience: Create a seamless experience for customers across multiple touchpoints, whether online, through mobile apps, or in-branch. The goal is for customers to enjoy a consistent experience wherever they choose to interact with the bank.
- Real-Time Interactions: Use AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to provide real-time customer support, ensuring that inquiries are answered instantly and personalized to the customer’s history.
By focusing on customer-centric innovation, banks can increase loyalty, attract new customers, and differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
- Data-Driven Decision Making
Data is at the core of modern banking, driving key decisions from risk management to customer engagement. Data-driven decision-making allows banks to optimize their operations, deliver personalized experiences, and improve financial outcomes.
Key Strategies:
- Advanced Analytics: Utilize big data and predictive analytics to assess customer behavior, predict trends, and make informed decisions about lending, risk management, and marketing.
- Customer Segmentation: Analyze data to segment customers more effectively, offering targeted products and services to specific groups. For example, younger customers may be more interested in mobile payments and budgeting tools, while older customers might prefer traditional banking products.
- Risk Assessment: Use data to improve credit scoring models and assess loan risks more accurately. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets to predict creditworthiness based on a wider range of factors.
By harnessing data, banks can improve decision-making, reduce risks, and enhance the overall customer experience.
- Operational Efficiency & Automation
Operational efficiency and automation are essential for driving cost reduction and improving service speed. By streamlining internal processes and reducing manual work, banks can focus on high-value tasks and offer more efficient services to customers.
Key Strategies:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automate repetitive, manual tasks such as data entry, loan processing, and account management to free up human resources for more complex tasks. RPA increases processing speed, reduces human error, and lowers costs.
- Process Optimization: Leverage analytics to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in internal processes. Streamlining these processes leads to faster decision-making and improved service delivery.
- Self-Service Platforms: Empower customers to handle simple tasks—such as transferring funds, checking balances, and paying bills—through intuitive mobile apps or online portals, reducing reliance on bank staff.
By automating tasks and optimizing processes, banks can increase productivity, reduce operational costs, and offer faster services to customers.
- Cybersecurity & Risk Management
As the banking sector digitizes, cybersecurity and risk management become increasingly important. With a growing amount of sensitive data being stored and transferred online, ensuring robust security measures is critical to maintaining customer trust and protecting against evolving threats.
Key Strategies:
- Advanced Threat Detection: Use AI and machine learning to identify unusual patterns and behaviors in real time. These systems can alert banks to potential fraud or cyberattacks, enabling faster responses.
- Multi-Layered Security: Implement a combination of encryption, firewalls, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and biometric security to protect customer data and prevent unauthorized access to accounts.
- Compliance & Data Protection: Ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR, PSD2, and other data protection laws. Secure handling of customer data not only ensures legal compliance but also protects against reputational damage.
A strong cybersecurity strategy is vital for safeguarding both the bank’s operations and its customers’ data, fostering trust in the digital banking environment.
- Integration & Interoperability
Integration and interoperability are essential for the seamless exchange of information between different systems, both within the bank and with external partners. As banking becomes more interconnected, ensuring systems can work together is crucial to providing a unified customer experience.
Key Strategies:
- API Development: Banks should adopt Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to connect with third-party services, fintech solutions, and payment providers. This allows the bank to offer new services quickly, such as peer-to-peer payments or integrated wealth management solutions.
- Open Banking: Open banking enables customers to securely share their financial data with third-party providers, opening up new opportunities for innovative services. By integrating with fintechs, banks can offer more personalized financial products and improve customer engagement.
- Data Integration: Implement integrated systems that allow for the seamless flow of data between front-end customer interfaces and back-end banking systems. This ensures that customer interactions are smooth and that employees have access to up-to-date information.
Effective integration and interoperability enable banks to offer more dynamic services, provide a better customer experience, and innovate faster in a competitive market.
- Innovation & Emerging Technologies
To stay ahead of the competition, banks must continually innovate by adopting emerging technologies that can revolutionize their operations and customer offerings. Technologies like blockchain, AI, and quantum computing present opportunities for disruptive innovation in banking.
Key Strategies:
- Blockchain: Implement blockchain for secure and transparent transactions, particularly in areas like cross-border payments, smart contracts, and fraud prevention.
- Quantum Computing: Although still in early stages, quantum computing promises to revolutionize areas such as risk modeling, fraud detection, and data encryption, providing banks with powerful new tools for processing complex calculations.
- AI-Powered Services: Explore new AI applications such as robo-advisors, which use algorithms to offer automated financial advice, or AI-based lending platforms that offer faster, more accurate credit assessments.
- Fintech Partnerships: Collaborating with fintech companies enables banks to quickly integrate emerging technologies into their existing infrastructure and access innovative solutions that can give them a competitive edge.
By embracing emerging technologies, banks can enhance their service offerings, improve efficiency, and provide cutting-edge solutions to meet the evolving demands of customers.
Conclusion
Digital transformation is essential for the future of banking, enabling financial institutions to meet the growing demands of tech-savvy customers and stay competitive. By focusing on customer-centric innovation, banks can offer personalized services that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Data-driven decision-making empowers banks to optimize operations and reduce risks, while operational efficiency and automation streamline processes, cutting costs and improving service delivery.
As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, robust cybersecurity and risk management strategies are crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining customer trust. Integration and interoperability through APIs and open banking allow banks to collaborate with fintechs, creating innovative products and services. Lastly, embracing emerging technologies like blockchain, AI, and quantum computing offers new opportunities to improve security, efficiency, and service offerings.
By implementing these strategies, banks can create a more agile, secure, and customer-focused future, positioning themselves to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.



