What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks within business processes.
These bots are designed to mimic human interactions with computer systems, applications, and data sources to perform tasks without human intervention.
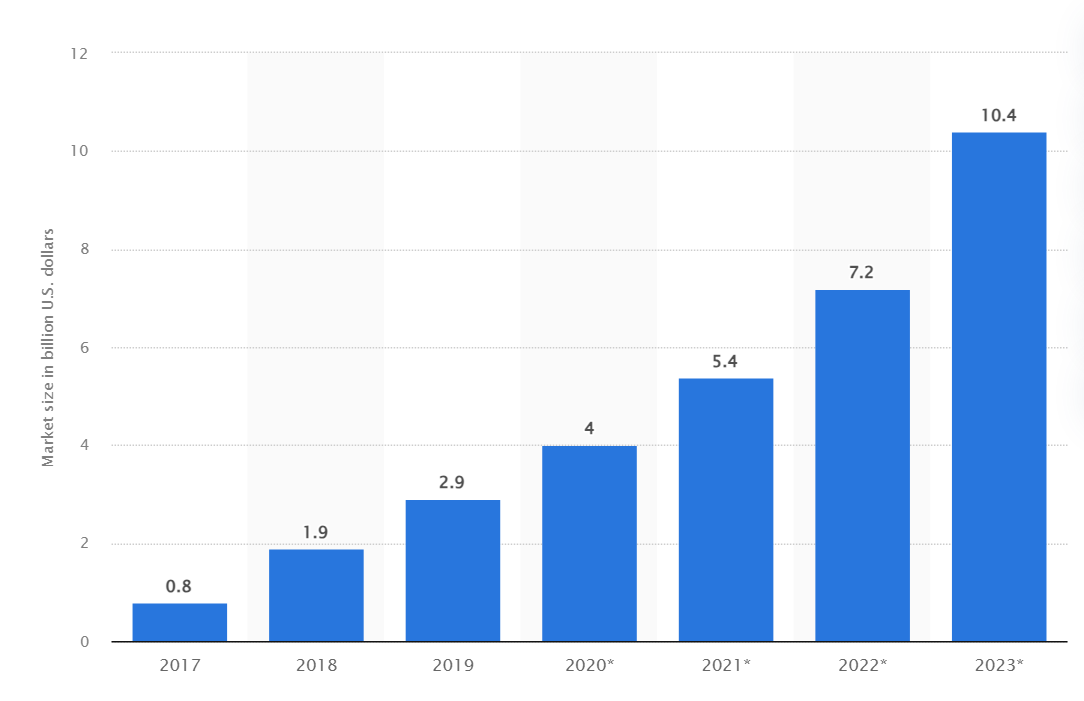
image source: Statista
According to Statista the global revenues within the realm of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are poised to exceed a substantial ten billion U.S. dollars in the year 2023. And the trend for this technology is only continuing to expand. Hop in to learn about RPA and the wonders it brings right now!
Let’s look at Example
Take a closer look at how deploying robotic process automation in the loan-processing function can prove transformational.
Today banks offer multiple touch points for customers to obtain loans. And while the front-end processes have become hassle-free for customers, the same cannot be said about the bank’s back-end processes. They continue to be labor-intensive, time-consuming and prone to human errors.
The back-end process for the bank worker ends up being a ton of paperwork: they must manually check individual credit scores, then manually enter various forms of data into the system, repeatedly copy/paste the data across multiple applications. These actions are extremely error-prone and consume a lot of resources.
This leaves little to no time for strategic tasks and therefore slows down the process as well as translating into employee burnout and poor customer experience.
Is there a way out of this situation? Certainly! Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can help solve these challenges. From loading and checking with the database to sending an automatic email – the burden of monotonous work can be taken away from the bank worker. Instead, they are left with a task that requires human strategic thinking and decision making.
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in banking
As we’ve already seen from the example above – one of the main RPA’s goals is efficiency. But it doesn’t stop there! Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers a range of significant benefits to the banking sector, transforming operations and enhancing overall customers’ experience.
Some of the key advantages of implementing RPA in banking include:
- Operational Efficiency: At the heart of RPA lies the promise of increased efficiency. Banks can automate labor-intensive and repetitive tasks, from data entry to account reconciliation, freeing up human resources for more strategic and creative tasks. This not only accelerates processes but also reduces the likelihood of errors, contributing to overall operational excellence.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: RPA is not just about streamlining back-office operations; it can significantly impact customer-facing processes as well. By automating customer onboarding, inquiries, and requests, banks can provide faster and more consistent services, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Cost Savings: Automation of processes through RPA translates into reduced operational costs. As manual interventions decrease, banks can optimize resource allocation and achieve cost savings in the long run.
- Regulatory Compliance: In the highly regulated banking industry, RPA can ensure adherence to complex regulatory requirements. By automating compliance checks and reporting, banks can reduce the risk of errors and penalties.
- Data Accuracy and Analytics: RPA enables accurate and consistent data handling across various systems. This standardized data can be leveraged for more informed decision-making and insightful analytics, contributing to a data-driven organizational culture.
Incorporating RPA into banking operations can fundamentally transform how financial institutions operate, enabling them to optimize processes, reduce costs, and provide superior customer service in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Use cases for RPA in Banking
The use cases of Robotic Process Automation can be incredibly varied and generally divided into two groups: frontend and backend. Frontend is mostly responsible for communication with the client and everything that comes with it. Backend on the other hand accounts for internal bank processes, such as data entry, fraud detection, etc.
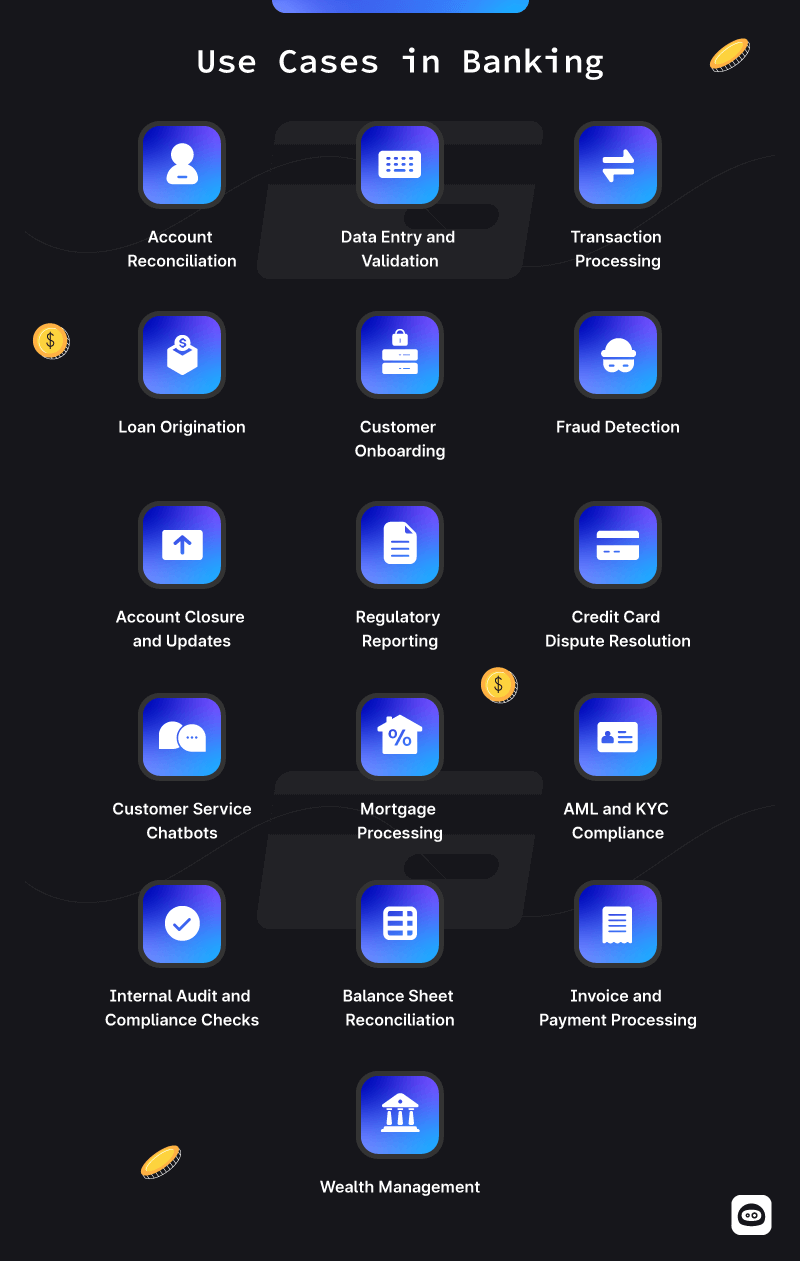
Use cases in Banking:
- Account Verification
- Data Entry and Validation.
- Transaction Processing
- Loan Processing
- Customer Onboarding
- Fraud Detection
- Account Closure and Updates
- Regulatory Reporting
- Credit Card Dispute Resolution
- Customer Service Chatbots
- Mortgage Processing
- AML and KYC Compliance
- Internal Audit and Compliance Checks
- Balance Sheet Reconciliation
- Invoice and Payment Processing
- Wealth Management
These use cases highlight the versatility and transformative potential of RPA in the banking industry, enabling financial institutions to optimize operations, improve customer service, and achieve greater efficiency across a wide spectrum of processes.
How to start with Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Let’s break it down how does the process of developing RPA for Banking actually happen.
Step 1: Figuring out the tasks. The first thing to do is figure out which tasks could benefit from RPA. You’ll want to prioritize these tasks based on how much they affect the company’s operations, efficiency, and the experience the customer gets.
Step 2: Blueprinting Solutions. Once you know which tasks you want to automate, the next step is to gather all the details you need to design your very own RPA solutions. This means figuring out how the process will flow, what goes in, what comes out, and what technology you need. Also, make sure your ideas are in line with the rules and regulations of the industry by checking with the compliance officer.
Step 3: Picking the right tools. Now, it’s time to choose the right tools to make your RPA dreams come true. Look for RPA tools that fit your needs, based on things like how much they cost, how well they can grow with your company, and how easily they can work with other systems.
Step 4: Implementation and Validation. Before you go all-in, it’s smart to test out your RPA tool in a real work situation. This helps you make sure it’s doing what you want it to do and getting great results.
Step 5: Full-scale Integration. Once you’re sure your RPA setup is working perfectly, you can introduce it to the real world of production. But remember, it’s not a “set it and forget it” technologie. You need to keep a close eye on how your RPA is doing and find ways to make it work even better if you can. This way, you can make sure it’s giving you the results you were hoping for.
Real world examples of RPA in banking
Deutsche Bank’s RPA for data processing
Deutsche Bank, along with its Blue Water Fintech Lab, has introduced a new program that simplifies business tasks using robots. This program, called Robotic Process Automation (RPA) commercialization, includes a useful tool known as a Data Processing and Reconciliation Solution. This tool, the bank’s first of its kind, helps companies handle their tasks more efficiently.
What’s interesting is that Deutsche Bank is the pioneer among international banks in China to present this innovative solution directly to its business clients. This smart tool, RPA, is like a digital assistant that assists company money managers in automating and simplifying their complex tasks. This makes it easier for these managers to offer quick and accurate information to their bosses, helping them make important decisions with confidence.
Societe Generale Bank’s RPA for Automatic Report Generation
Societe Generale Bank Brazil is one of the leading suppliers of financial services in Brazil. They offer consultancy and other services to both corporate and institutional clients.
At Societe Generale Bank Brazil, the staff relies on important reports and analysis to handle their daily tasks. These reports used to be time-consuming to put together, taking up a large portion of their day. This left them with less time for other important tasks.
However, things changed when they discovered a versatile solution called Automate Plus, developed by Fortra. They teamed up with SicoloS Technology and employed the software robots of Automate to tackle crucial report-related tasks during the night. This clever move has transformed their routine. They now step into the office with all the necessary tools to perform their duties effectively, ensuring top-notch service for their clients.
The introduction of robotic process automation (RPA) has not only saved them a significant amount of time but has also allowed them to scale their operations. Previously, a single employee had to dedicate up to 6 hours each day to these tasks. With RPA in place, these tasks are now automated, freeing up their team to engage in more intricate and value-driven activities. This shift enables them to enhance their client service and tackle more challenging endeavors.
Axis Bank’s RPA
Axis Bank embarked on its RPA journey by tackling straightforward tasks. They began by setting up the first set of tasks that could benefit from automation: handling salary processing via STP upload, managing cheque processing and clearing, and processing service requests for tasks like changing addresses or making nominations.
As their RPA journey evolved, Axis Bank expanded its automation efforts to encompass internal banking functions. This involved streamlining invoice processing within the finance department, simplifying intricate reports essential for daily operations, and ensuring seamless reconciliation to enhance operational control. Additionally, they utilized RPA for risk-based triggers that monitor the general ledger, as well as for processing vouchers tied to vendor payments and handling employee travel claims.
Challenges associated with RPA technology
While Robotic Process Automation (RPA) holds immense potential for enhancing business processes, it also presents several challenges that organizations must address to ensure successful implementation and utilization.
These challenges encompass various aspects of technology integration, organizational change, and operational considerations.
Here are some of the key challenges that might arise with RPA technology:
- Process Complexity: Implementing RPA for highly complex and dynamic processes can be intricate. Defining automation workflows, handling exceptions, and accommodating nuanced decision-making can pose difficulties.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating RPA with existing legacy systems and diverse software applications requires careful planning and coordination to ensure seamless data flow and interoperability.
- Change Management: Introducing automation through RPA may lead to resistance or concerns among employees who fear job displacement or shifts in responsibilities. Effective change management strategies are crucial to address these apprehensions.
- Data Security and Privacy: As RPA bots handle sensitive data and perform critical tasks, ensuring data security, privacy, and compliance with regulations becomes paramount. Unauthorized access or breaches can lead to severe consequences.
- Scalability and Maintenance: As RPA initiatives expand, managing an increasing number of bots and maintaining their functionality, compatibility, and performance levels can become complex and resource intensive.
- Process Standardization: RPA works best with standardized and well-defined processes. In cases where processes vary significantly, standardizing them to fit RPA requirements can be a challenge.
- Bot Monitoring and Management: Regular monitoring and management of RPA bots are essential to ensure they perform as intended and respond to changes or exceptions appropriately.
- Initial Investment: While RPA offers long-term cost savings, there is an initial investment required for software, hardware, training, and infrastructure setup.
- Lack of Technical Expertise: Organizations may face challenges in recruiting and retaining skilled professionals who are proficient in RPA development, configuration, and maintenance.
- Governance and Compliance: Establishing governance policies and compliance standards for RPA activities is necessary to maintain transparency, accountability, and adherence to industry regulations.
- Reliability and Dependency: Over-reliance on RPA without contingency plans can become problematic if bots encounter technical issues or errors, leading to disruptions in critical processes.
- Cultural Alignment: Integrating RPA into the organization’s culture and ensuring that employees embrace the technology as a tool to enhance their work can be a cultural challenge.
Navigating these challenges requires a strategic and comprehensive approach. Organizations must proactively address technical, operational, and human factors to harness the full potential of RPA and drive successful digital transformation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Robotic Process Automation has emerged as a powerful and transformative force within the banking sector, offering plenty of benefits, innovative use cases, and unique challenges. The integration of this technology into banking operations brings efficiency gains, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer experiences. Through the automation of routine and rule-based tasks, banks can redirect their human workforce towards higher-value activities that demand strategic thinking and personalized customer interactions.
The use cases of RPA in banking can be very diverse and therefore impactful. From transaction processing, and account reconciliation to fraud detection, regulatory compliance, and customer service – Robotic Process Automation has proven its versatility across various functions. Moreover, its ability to facilitate quicker decision-making through data-driven insights in some cases paired with AI processing even further underscores its value in modern banking operations.
However, the adoption of RPA does not come without its challenges. Implementation problems with processes such as optimization, technology integration, and workforce reskilling, demand a very careful navigation. In addition to that, there is a need to address data security, compliance, and work out a potential job displacement. All of this requires a well-considered approach that includes time invested in learning the technology and calculating the potential risks.
In the fast-evolving landscape banking sector, Robotic Process Automation might serve as a catalyst for further digital transformation, as well as empower financial institutions to remain competitive and agile. As banks continue to leverage RPA’s capabilities to innovate and drive operational excellence, a balanced approach that embraces its benefits while proactively addressing challenges will be key to realizing its full potential in reshaping the future of banking.
FAQ
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is used in fintech for automating repetitive tasks like data entry, transaction processing, customer onboarding, and compliance checks. It improves efficiency, accuracy, and customer experience, while also aiding in fraud detection, reporting, and internal processes.
RPA in banking optimizes processes, minimizes errors, increases accuracy, and enhances customer satisfaction. It allows banking professionals to focus on high-value tasks that require human judgment and expertise, leading to a more efficient and effective financial institution.
RPA is focused on automating routine and repetitive tasks, while AI is centered around mimicking human intelligence and making predictions or decisions based on data. In many cases, RPA and AI can complement each other within the finance industry, with RPA handling process automation and AI adding intelligence and insights to various financial tasks and processes.
Process selection is a critical initial step in the implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) within banks. It involves identifying and prioritizing specific business processes that are suitable for automation using RPA technology. The goal is to select repetitive, rule-based processes that will provide substantial benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.



